The Chinese Church in Greater Boston
The Chinese Church in Greater Boston
by Dan Johnson, Ph.D., and Kaye Cook, Ph.D., with Rev. T. K. Chuang, Ph.D.
From just two Chinese churches in greater Boston 50 years ago, the number has grown to more than 25 congregations serving an expanding Chinese population. The growth of the Chinese church in and around the Boston area is something to celebrate. Its strength and integrity, and the quality of its network—unified for prayer, for youth and college ministry, and for international missions, among others—stand as a model for other immigrant churches and indeed for other indigenous churches as well.
What does the Chinese church in Boston look like? What are the strengths and weaknesses as well as the clear opportunities and threats that face these churches at the start of the 21st century?
Students and immigration
In 2016, as many as 350,000 students and visiting scholars from China were actively working in the U.S., a population that dwarfed the number who came from Taiwan and Hong Kong. Over 30% of all international students studying in the U.S. are from China, according to the Institute of International Education (www.iie.org). Not surprisingly, thousands of these are regularly drawn toward Boston-area colleges and universities, as well as to the opportunities available to them in the region’s “knowledge economy.” The 2010 U.S. Census found that the Chinese population of the greater Boston area numbered nearly 123,000, some two and one-half times as many as were present just 20 years before.
Of these, it is estimated somewhere between 5% and 8% identify as Christian. Many of the Chinese newcomers to the area each year are already Christian when they arrive, in which case the Chinese church provides them a primary community to ease the transition to life in a new place. The others are generally quite open to the Christian message. Indeed, to this day Chinese students are routinely found to be the most receptive group to Christian outreach efforts on local campuses. As a consequence, this influx of new immigrants and students from China has brought significant numeric growth to the Chinese church over the last 25 years. Most notably, most of the established Mandarin-speaking congregations experienced 20-80% growth over the decade of the 1990s. Such growth has generally plateaued since then, but new church plants have continued apace.
Church planting
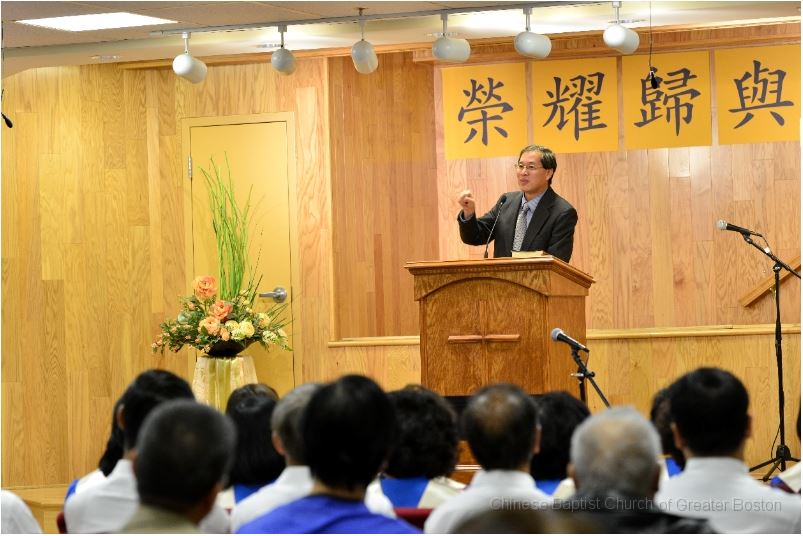
Chinese Church of Greater Boston
Since 1990, more than fifteen new Chinese churches have been planted, mostly Mandarin-speaking, and mostly serving small, geographically distinct communities and congregations. From a mere two Chinese churches in the entire region 50 years ago, today the Chinese church in the greater Boston area includes more than 25 separate congregations. The steady stream of newcomers from mainland China has also reshaped the character of the Chinese church in the region. The most obvious change is the shift from predominantly Cantonese-speaking congregations to predominantly Mandarin-speaking ones.
As noted, most Chinese church plants over the last 25 years have been established to serve newly settled Mandarin-speaking communities. In a few other instances, older churches that originally served Cantonese-speakers have seen their ministries to the Mandarin-speaking community expand dramatically while their Cantonese populations have dwindled or disappeared altogether. This transformation is more than just linguistic in nature. The Mandarin-speaking newcomers from mainland China are mostly first-generation Christians and new converts. Their formative experiences were generally in a more materialist, atheistic culture, and they often identify primarily with the values and orientations of the academic and professional cultures in which they are immersed. This general lack of church experience has made basic biblical education and discipleship a more pressing need in the congregations that serve them. The fact that very few are ready to step into leadership and ministry roles in the church also creates a gulf between the new generation of Chinese Christians and the established church leadership. By virtue of their formal theological training, deep spiritual commitments, and long habituation in the relatively more developed Christian communities of Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the United States, church leaders in Boston’s Chinese communities often find it harder to connect with the felt needs and mentality of their newest congregants. The challenge is made even more difficult by the fact that many of Boston’s second-generation Chinese Christians, who might otherwise be there to welcome these newcomers into the Chinese church, have chosen instead to become members of American or Asian-American churches.
These social dynamics provide the backdrop for the analysis that follows of the current state of the Chinese Christian church in the greater Boston area. Beyond its identifiable strengths and weaknesses, and the clear opportunities and threats that it faces, is the simple realization that this is a seventy-year-old church undergoing a significant growth-induced transformation.
STRENGTHS
Interchurch collaboration
One of the greatest strengths of the Chinese church in the Boston area is that the various churches that comprise it mostly get along and have forged important collaborative relationships. The largely non-denominational character of the churches has minimized theological frictions between them, and the numerous personal ties between individuals across congregations—often forged in common spaces, such as the Boston Chinese Bible Study Group at MIT—help to smooth inter-congregational relationships more generally. The collaborative efforts that have resulted include regular prayer gatherings, shared missions programs, joint sponsorship of career missionaries, evangelistic meetings, and a gospel camp. Such programs are often initiated and organized by individual churches and then opened up to other area churches, as the Chinese Bible Church of Greater Boston (Lexington) did for many years with its annual gospel camp. The fact that even the largest churches in the community (including the Boston Chinese Evangelical Church and CBCGB) have been willing to sponsor and participate in such joint efforts has gone a long way toward ensuring their success.
Cultural centers
The Chinese church also serves as a primary reference group for many newcomers to the area, as they have become some of the most active and well-organized social institutions within the Chinese community. Many new immigrants naturally turn to the church for help. The familiar language, cultural references, and social structures they encounter in the church are key factors in securing their sense of identity when all else around them is unsettled. The larger churches’ programs for children and youth also attract immigrant families.
An ethic of evangelism
Another strength of the Chinese church in the area is the ethic of active evangelism that has long been cultivated in its constituent congregations. For many years, this ethic has animated large-scale, seeker sensitive programs that have encouraged and enabled church members to put it into practice, aggressively evangelizing their kinspeople. Many of these programs—such as the CBCGB’s annual gospel camp—have since disappeared, and it remains an open question whether the evangelistic focus of the church can be sustained in their absence. Nonetheless, the inspiring heritage of evangelistic activity is itself a strength of the Chinese church in and around Boston.
A place for Mandarin-speaking immigrants
Lastly, the very fact that so many Chinese churches in the area were either founded to serve Mandarin speakers or have since developed vibrant ministries for the Mandarin community is a significant strength. Not every Chinese community around the world is so prepared to welcome and minister to the steady stream of Chinese immigrants from the mainland that inundates them today. The Boston area’s dense network of Mandarin-speaking churches marked by an intellectual richness and a strong professional class leaves it well positioned to meet the needs of the future church in Boston.
WEAKNESSES
Cultural Isolation
Historically, a lack of interaction with people who are not Chinese has probably been the most significant weakness in the Chinese church in and around Boston. The founding members of the most established churches have minimal contact, if any, with the non-Chinese community. Moreover, Chinese churches have rarely tried to hold joint events with other groups, with CBCGB being the one noteworthy exception. Such isolation from the surrounding society has been an obvious problem for the further development of the Chinese churches. This problem has abated somewhat, however, with the infusion of a larger professional class into the church over the last 25 years. This population generally has stronger ties to the secular professional networks in which they are immersed than to the ethnically-rooted churches they happen to attend.
Yet with this more worldly orientation comes the other problem of a widespread shallowness in the understanding of and commitment to the historic Christian faith. The church is in dire need of addressing this problem through basic Christian education and discipleship.
The generational divide
Another weakness besetting the established Chinese church is the deepening of the generational divides that separate older from younger Christians, first-generation immigrants from second-generation, and so on. While such divides have always been present, in recent years they have grown in ways that lead to the exodus from the Chinese church of those who were brought up in it. As noted, many of those who leave find their way to American churches that seem to address their needs more effectively. Many others, however, end up leaving the church altogether.
Small churches
Lastly, the problem of small congregational sizes hampered by resource constraints remains as prevalent today as ever. While the explosive growth of the last 25 years clearly benefited a handful of churches, the emergence of smaller congregations with an emphasis on ministry to their particular local communities has left many vulnerable. More than half of the Chinese congregations have less than 100 attendees, and these struggle financially with limited personnel. Many of them face such problems as a lack of volunteer workers, limited or no youth and children’s programs, and the difficulty of reaching a minimum threshold size to sustain growth. For some, it is challenging enough to remain viable. In this respect, a revival of the spirit of collaboration among the Chinese churches, with conscientious participation by the larger churches in the area, may be a key to the continued survival of these vital congregations.
OPPORTUNITY
Immigration continues
The steady and deepening stream of Chinese immigration from the mainland shows no signs of slowing in the coming years. The educational environment and the high-tech job market in the area will continue to attract many, providing an ongoing inflow of immigrants. Some of these newcomers are eager to attend a church, but many are not. Given the numbers, the proliferation of Chinese churches over the last few decades may continue, but careful observation and strategic planning will be needed to identify emerging pockets of Chinese newcomers who could be well served by a local Chinese church.
Changing cultures and thought systems
The arrival of more recent groups of graduate school students, scholars, and other professionals pose new challenges based on their distinctive generational experience and worldview. The factors that led many Chinese radicals of an earlier generation to explore and embrace Christianity—namely, the simple impulse to distance oneself from Maoism and communism, or the desire to secure an identity and existential anchor by identifying with “Western” institutions and thought systems, or even the hope of getting ahead in the modern world by adopting ways of thinking that are more prevalent outside China—have all been undermined in various ways.
The Chinese immigrants of today have grown up in a consumerist society that understands itself to have arrived, fully modern and ready to conquer the world. To the extent that such a mindset generates less of a felt need to turn to God, we might expect the boom in Chinese conversions to Christianity in the years following the Cultural Revolution and the massacre in Tienanmen Square will slow. Yet the Chinese church should seize it as an opportunity to develop new ways of sharing the Gospel so that it will be heard by those who have new ears.
Collaborative missions and outreach
Finally, the opportunity still remains for the Chinese church in greater Boston to develop a more aggressive, coordinated missions strategy that reaches beyond New England. These churches have a history of joining together for small-scale, collaborative missions programs, both short-term and long-term. Their initiatives include the now 20-year-old “Boston to Beijing” program for sending teams to teach English in mainland China, short-term missions/outreach groups working in England, and the joint sponsorship of career missionaries by multiple congregations. While all of this represents a good start, more can be done. Especially in light of the common passion of new converts to share their faith with others, a more deliberate mobilization of the Chinese churches to engage missions efforts in China and among the Chinese diaspora could help to draw those new converts more deeply into the activities of the church. Of course, when it comes to engaging in missions work or establishing relationships with churches in communist China, the larger the effort the more carefully its participants must tread. Even so, the opportunities for mutual support, growth, and understanding are too significant to pass up.
THREATS
Curiously, the most significant threats facing the Chinese church in the Boston area may be those imported from mainland China. The general lack of theological training within the Chinese house church movement and the prevalence of Buddhist, Taoist and folk religious traditions in most areas served by the house church make it a potential breeding ground for syncretistic beliefs and practices that can lead their followers away from the historic Christian faith. Insofar as many immigrant Christians from house churches on the Chinese mainland are incorporated into local congregations, the potential exists for such problematic religious understandings to gain a foothold here. While the generally high level of education in the Boston Chinese church of today perhaps mitigates this possibility, it is nonetheless a matter that warrants vigilance.
CONCLUSION
The growth of the Chinese church in and around the Boston area is something to celebrate. Its strength and integrity, and the quality of its network—unified for prayer, for youth and college ministry, and for international missions, among others—stand as a model for other immigrant churches and indeed for other indigenous churches as well. Although the Chinese church is relatively isolated from those around it, its impact is significant. Its unique history in a world educational hub and key center of the early evangelical missions movement has meant mature leadership in a world-wide Chinese church that is relatively young and whose leadership is often relatively untrained. Its extensive growth out of local campus Bible study groups gives it access to a more professional population that poses unique challenges but also unique opportunities. Add in the fact that it has unparalleled opportunities to reach with the necessary care and discretion into mainland China—one of the largest and most receptive populations for evangelical outreach today—and it is clear that the Chinese church in the greater Boston area is poised to play an outsized role in shaping the future of the church world-wide.
_________
by Dan Johnson, Ph.D., and Kaye Cook, Ph.D., both of Gordon College, with T. K. Chuang, Ph.D., former senior pastor, Chinese Bible Church of Greater Boston. This chapter was originally written by T. K. Chuang and published as part of Emmanuel Gospel Center’s New England’s Book of Acts (2007). Extensively updated in 2016 by Dan Johnson and Kaye Cook in conversation with Rev. Dr. Chuang.
_________
More resources:
Map. For an interactive map of Chinese churches in Greater Boston, click here.
Church listing. For a listing of Chinese churches in Greater Boston, click here.




![Ethiopian Churches in Greater Boston [map]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/57ff1c7ae58c62d6f84ba841/1506113852983-TSLLC1FENTJJGZYIO7MM/orthodox+cross+church.jpeg)





“In June of 1972, I was discouraged because a year had gone by since I had graduated from seminary, and I hadn’t raised a penny to go back to Haiti, which had been my goal. So after preaching at a church in New York City, two ladies asked me whether they could join my wife and me for a night of prayer.